As already mentioned, a hypothesis is an assumption that may prove to be either correct or incorrect. It is possible to arrive at an incorrect conclusion about a hypothesis for a variety of reasons. Incorrect conclusions about the validity of a hypothesis may be drawn if:
- the study design selected is faulty;
- the sampling procedure adopted is faulty;
- the method of data collection is inaccurate;
- the analysis is wrong;
- the statistical procedures applied are inappropriate; or
- the conclusions drawn are incorrect.
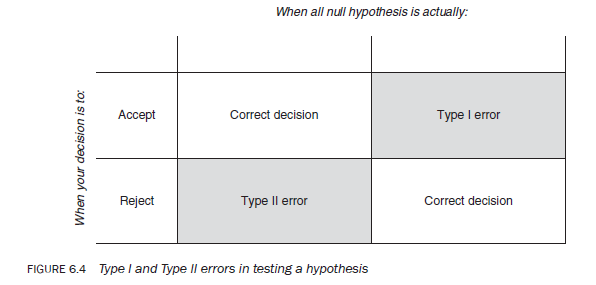
Any, some or all of these aspects of the research process could be responsible for the inadvertent introduction of error in your study, making conclusions misleading. Hence, in the testing of a hypothesis there is always the possibility of errors attributable to the reasons identified above. Figure 6.4 shows the types of error that can result in the testing of a hypothesis.
Hence, in drawing conclusions about a hypothesis, two types of error can occur:
- Rejection of a null hypothesis when it is true. This is known as a Type I error.
- Acceptance of a null hypothesis when it is false. This is known as a Type II error.
Source: Kumar Ranjit (2012), Research methodology: a step-by-step guide for beginners, SAGE Publications Ltd; Third edition.

29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
30 Jul 2021