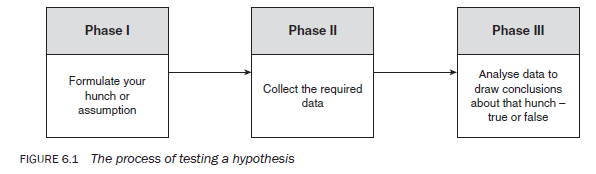
To test a hypothesis you need to go through a process that comprises three phases: (1) constructing a hypothesis; (2) gathering appropriate evidence; and (3) analysing evidence to draw conclusions as to its validity. Figure 6.1 shows this process diagrammatically. It is only after analysing the evidence that you can conclude whether your hunch or hypothesis was true or false. When concluding about a hypothesis, conventionally, you specifically make a statement about the correctness or otherwise of a hypothesis in the form of ‘the hypothesis is true’ or ‘the hypothesis is false’. It is therefore imperative that you formulate your hypotheses clearly, precisely and in a form that is testable. In arriving at a conclusion about the validity of your hypothesis, the way you collect your evidence is of central importance and it is therefore essential that your study design, sample, data collection method(s), data analysis and conclusions, and communication of the conclusions be valid, appropriate and free from any bias.
Source: Kumar Ranjit (2012), Research methodology: a step-by-step guide for beginners, SAGE Publications Ltd; Third edition.

29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
30 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
30 Jul 2021