Whether we accept it or not, we all make value judgements constantly in our daily lives: ‘This food is excellent’; ‘I could not sleep well last night’; ‘I do not like this’; and ‘I think this is wonderful’. These are all judgements based upon our own preferences, indicators or assessment. Because these explain feelings or preferences, the basis on which they are made may vary markedly from person to person. There is no uniform yardstick with which to measure them. A particular food may be judged ‘excellent’ by one person but ‘awful’ by another, and something else could be wonderful to one person but ugly to another. When people express these feelings or preferences, they do so on the basis of certain criteria in their minds, or in relation to their expectations.
If you were to question them you will discover that their judgement is based upon indicators and/or expectations that lead them to conclude and express a particular opinion.
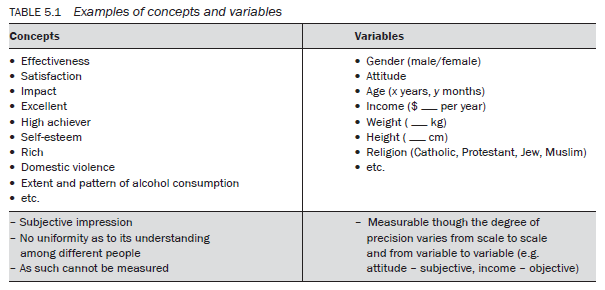
- Let us consider this in a professional context:
- ‘This programme is effective.’
- ‘This programme is not effective.’
- ‘We are providing a quality service to our clients.’
- ‘This is a waste of time.’
- ‘In this institution women are discriminated against.’
- ‘There is no accountability in this office.’
- ‘This product is not doing well.’
These are not preferences per se; these are judgements that require a sound basis on which to proclaim. For example, if you want to find out if a programme is effective, if a service is of quality or if there is discrimination, you need to be careful that such judgements have a rational and sound basis. This warrants the use of a measuring mechanism and it is in the process of measurement that knowledge about variables plays an important role.
An image, perception or concept that is capable of measurement – hence capable of taking on different values – is called a variable. In other words, a concept that can be measured is called a variable. According to Kerlinger, ‘A variable is a property that takes on different values. Putting it redundantly, a variable is something that varies … A variable is a symbol to which numerals or values are attached’ (1986: 27). Black and Champion define a variable as ‘rational units of analysis that can assume any one of a number of designated sets of values’ (1976: 34). A concept that can be measured on any one of the four types of measurement scale, which have varying degrees of precision in measurement, is called a variable (measurement scales are discussed later in this chapter).
However, there are some who believe that scientific methods are incapable of measuring feelings, preferences, values and sentiments. In the author’s opinion most of these things can be measured, though there are situations where such feelings or judgements cannot be directly measured but can be measured indirectly through appropriate indicators. These feelings and judgements are based upon observable behaviours in real life, though the extent to which the behaviours reflect their judgements may vary from person to person. Cohen and Nagel express their opinion in the following words:
There are, indeed, a great many writers who believe that scientific method is inherently inapplicable to such judgements as estimation or value, as ‘This is beautiful’, ‘This is good’ or ‘This ought to be done’ … all judgements of the latter type express nothing but feelings, tastes or individual preferences, such judgements cannot be said to be true or false (except as descriptions of the personal feelings of the one who utters them) . Almost all human discourse would become meaningless if we took the view that every moral or aesthetic judgement is no more true or false than any other. (1966: 352).
Source: Kumar Ranjit (2012), Research methodology: a step-by-step guide for beginners, SAGE Publications Ltd; Third edition.

30 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
29 Jul 2021
30 Jul 2021
30 Jul 2021