To be a marketer, you need to understand what marketing is, how it works, who does it, and what is marketed.
1. WHAT IS MARKETING?
Marketing is about identifying and meeting human and social needs. One of the shortest good definitions of marketing is “meeting needs profitably.” When Google recognized that people needed to more effectively and efficiently access information on the Internet, it created a powerful search engine that organized and prioritized queries. When IKEA noticed that people wanted good furnishings at substantially lower prices, it created knockdown furniture. These two firms demonstrated marketing savvy and turned a private or social need into a profitable business opportunity.
The American Marketing Association offers the following formal definition: Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.8 Coping with these exchange processes calls for a considerable amount of work and skill. Marketing management takes place when at least one party to a potential exchange thinks about the means of achieving desired responses from other parties. Thus, we see marketing management as the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value.
We can distinguish between a social and a managerial definition of marketing. A social definition shows the role marketing plays in society; for example, one marketer has said that marketing’s role is to “deliver a higher standard of living.” Here is a social definition that serves our purpose: Marketing is a societal process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering, and freely exchanging products and services of value with others. Cocreation of value among consumers and with businesses and the importance of value creation and sharing have become important themes in the development of modern marketing thought.9
Managers sometimes think of marketing as “the art of selling products,” but many people are surprised when they hear that selling is not the most important part of marketing! Selling is only the tip of the marketing iceberg. Peter Drucker, famed management theorist, put it this way:10
There will always, one can assume, be need for some selling. But the aim of marketing is to make selling superfluous. The aim of marketing is to know and understand the customer so well that the product or service fits him and sells itself. Ideally, marketing should result in a customer who is ready to buy. All that should be needed then is to make the product or service available.
When Nintendo designed its Wii game system, when Apple launched its iPad tablet computer, and when Toyota introduced its Prius hybrid automobile, these manufacturers were swamped with orders because they had designed the right product, based on careful marketing homework about consumers, competition, and all the external factors that affect cost and demand.
2. WHAT IS MARKETED?
Marketers market 10 main types of entities: goods, services, events, experiences, persons, places, properties, organizations, information, and ideas. Let’s take a quick look at these categories.
GOODS Physical goods constitute the bulk of most countries’ production and marketing efforts. Each year, U.S. companies market billions of fresh, canned, bagged, and frozen food products and millions of cars, refrigerators, televisions, machines, and other mainstays of a modern economy.
SERVICES As economies advance, a growing proportion of their activities focuses on the production of services. The U.S. economy today produces a services-to-goods mix of roughly two-thirds to one-third.11 Services include the work of airlines, hotels, car rental firms, barbers and beauticians, maintenance and repair people, and accountants, bankers, lawyers, engineers, doctors, software programmers, and management consultants. Many market offerings mix goods and services, such as a fast-food meal.
EVENTS Marketers promote time-based events, such as major trade shows, artistic performances, and company anniversaries. Global sporting events such as the Olympics and the World Cup are promoted aggressively to companies and fans. Local events include craft fairs, bookstore readings, and farmer’s markets.
EXPERIENCES By orchestrating several services and goods, a firm can create, stage, and market experiences. Walt Disney World’s Magic Kingdom lets customers visit a fairy kingdom, a pirate ship, or a haunted house.
Customized experiences include a week at a baseball camp with retired baseball greats, a four-day rock and roll fantasy camp, and a climb up Mount Everest.
PERSONS Artists, musicians, CEOs, physicians, high-profile lawyers and financiers, and other professionals often get help from marketers.12 Many athletes and entertainers have done a masterful job of marketing themselves—NFL quarterback Peyton Manning, talk show veteran Oprah Winfrey, and rock and roll legends The Rolling Stones. Management consultant Tom Peters, himself a master at self-branding, has advised each person to become a “brand.”
PLACES Cities, states, regions, and whole nations compete to attract tourists, residents, factories, and company headquarters.13 Place marketers include economic development specialists, real estate agents, commercial banks, local business associations, and advertising and public relations agencies. The Las Vegas Convention & Visitors Authority has met with much success with its provocative ad campaign “What Happens Here, Stays Here,” portraying Las Vegas as “an adult playground.”
PROPERTIES Properties are intangible rights of ownership to either real property (real estate) or financial property (stocks and bonds). They are bought and sold, and these exchanges require marketing. Real estate agents work for property owners or sellers, or they buy and sell residential or commercial real estate. Investment companies and banks market securities to both institutional and individual investors.
ORGANiZATIONS Museums, performing arts organizations, corporations, and nonprofits all use marketing to boost their public images and compete for audiences and funds. Some universities have created chief marketing officer (CMO) positions to better manage their school identity and image, via everything from admission brochures and Twitter feeds to brand strategy.14
Oprah Winfrey has built a personal brand worth billions which she has used across many lines of business.
INFORMATION Information is essentially what books, schools, and universities produce, market, and distribute at a price to parents, students, and communities. Firms make business decisions using information supplied by organizations like Thomson Reuters: “We combine industry expertise with innovative technology to deliver critical information to leading decision makers in the financial, legal, tax and accounting, healthcare, science and media markets, powered by the world’s most trusted news organization.”15
IDEAS Every market offering includes a basic idea. Charles Revson of Revlon once observed: “In the factory we make cosmetics; in the drugstore we sell hope.” Products and services are platforms for delivering some idea or benefit. Social marketers promote such ideas as “Friends Don’t Let Friends Drive Drunk” and “A Mind Is a Terrible Thing to Waste.”
3. WHO MARKETS?
MARKETERS AND PROSPECTS A marketer is someone who seeks a response—attention, a purchase, a vote, a donation—from another party, called the prospect. If two parties are seeking to sell something to each other, we call them both marketers.
Marketers are skilled at stimulating demand for their products, but that’s a limited view of what they do. They also seek to influence the level, timing, and composition of demand to meet the organization’s objectives. Eight demand states are possible:
- Negative demand—Consumers dislike the product and may even pay to avoid it.
- Nonexistent demand—Consumers may be unaware of or uninterested in the product.
- Latent demand—Consumers may share a strong need that cannot be satisfied by an existing product.
- Declining demand—Consumers begin to buy the product less frequently or not at all.
- Irregular demand—Consumer purchases vary on a seasonal, monthly, weekly, daily, or even hourly basis.
- Full demand—Consumers are adequately buying all products put into the marketplace.
- Overfull demand—More consumers would like to buy the product than can be satisfied.
- Unwholesome demand—Consumers may be attracted to products that have undesirable social consequences.
In each case, marketers must identify the underlying cause(s) of the demand state and determine a plan of action to shift demand to a more desired state.
MARKETS Traditionally, a “market” was a physical place where buyers and sellers gathered to buy and sell goods. Economists describe a market as a collection of buyers and sellers who transact over a particular product or product class (such as the housing market or the grain market).
Five basic markets and their connecting flows are shown in Figure 1.1. Manufacturers go to resource markets (raw material markets, labor markets, money markets), buy resources and turn them into goods and services, and sell finished products to intermediaries, who sell them to consumers. Consumers sell their labor and receive money with which they pay for goods and services. The government collects tax revenues to buy goods from resource, manufacturer, and intermediary markets and uses these goods and services to provide public services. Each nation’s economy, and the global economy, consists of interacting sets of markets linked through exchange processes.
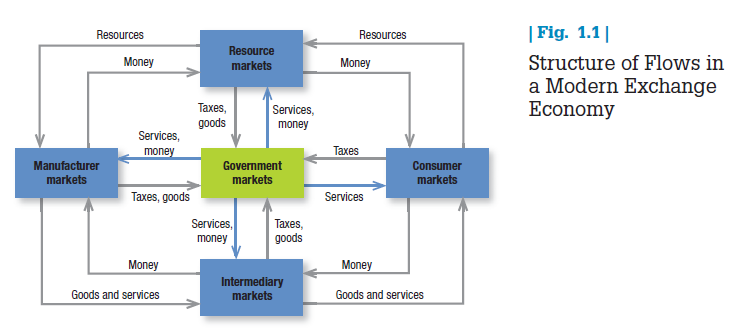
Marketers view sellers as the industry and use the term market to describe customer groups. They talk about need markets (the diet-seeking market), product markets (the shoe market), demographic markets (the “millennium” youth market), geographic markets (the Chinese market), or voter markets, labor markets, and donor markets.
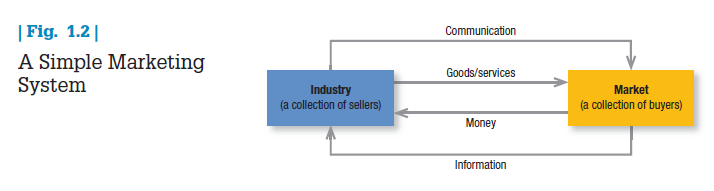
Figure 1.2 shows how sellers and buyers are connected by four flows. Sellers send goods and services and communications such as ads and direct mail to the market; in return they receive money and information such as customer attitudes and sales data. The inner loop shows an exchange of money for goods and services; the outer loop shows an exchange of information.
KEY CUSTOMER MARKETS Consider the following key customer markets: consumer, business, global, and nonprofit.
Consumer Markets Companies selling mass consumer goods and services such as juices, cosmetics, athletic shoes, and air travel establish a strong brand image by developing a superior product or service, ensuring its availability, and backing it with engaging communications and reliable performance.
Business Markets Companies selling business goods and services often face well-informed professional buyers skilled at evaluating competitive offerings. Advertising and Web sites can play a role, but the sales force, the price, and the seller’s reputation may play a greater one.
Global Markets Companies in the global marketplace navigate cultural, language, legal, and political differences while deciding which countries to enter, how to enter each (as exporter, licenser, joint venture partner, contract manufacturer, or solo manufacturer), how to adapt product and service features to each country, how to set prices, and how to communicate in different cultures.
Nonprofit and Governmental Markets Companies selling to nonprofit organizations with limited purchasing power such as churches, universities, charitable organizations, and government agencies need to price carefully. Much government purchasing requires bids; buyers often focus on practical solutions and favor the lowest bid, other things equal.16
Source: Kotler Philip T., Keller Kevin Lane (2015), Marketing Management, Pearson; 15th Edition.

Very interesting subject, thankyou for putting up. “Integrate what you believe into every single area of your life.” by Meryl Streep.