For more than 30 years, relational database technology has been the gold standard. Cloud computing, unprecedented data volumes, massive workloads for web services, and the need to store new types of data require
database alternatives to the traditional relational model of organizing data in the form of tables, columns, and rows. Companies are turning to “NoSQL” non-relational database technologies for this purpose. Non-relational database management systems use a more flexible data model and are designed for managing large data sets across many distributed machines and for easily scaling up or down. They are useful for accelerating simple queries against large volumes of structured and unstructured data, including web, social media, graphics, and other forms of data that are difficult to analyze with traditional SQL-based tools.
There are several different kinds of NoSQL databases, each with its own technical features and behavior. Oracle NoSQL Database is one example, as is Amazon’s SimpleDB, one of the Amazon Web Services that run in the cloud. SimpleDB provides a simple web services interface to create and store multiple data sets, query data easily, and return the results. There is no need to predefine a formal database structure or change that definition if new data are added later.
MetLife’s MongoDB open source NoSQL database brings together data from more than 70 separate administrative systems, claims systems, and other data sources, including semi-structured and unstructured data, such as images of health records and death certificates. The NoSQL database can handle structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information without requiring tedious, expensive, and time-consuming database mapping to normalize all data to a rigid schema, as required by relational databases.
1. Cloud Databases and Distributed Databases
Among the services Amazon and other cloud computing vendors provide are relational database engines. Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) offers MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, PostgreSQL, or Amazon Aurora as database engines. Pricing is based on usage. Oracle has its own Database Cloud Services using its relational Oracle Database, and Microsoft Azure SQL Database is a cloud-based relational database service based on the Microsoft SQL Server DBMS. Cloud-based data management services have special appeal for web-focused startups or small to medium-sized businesses seeking database capabilities at a lower cost than in-house database products.
Google now offers its Spanner distributed database technology as a cloud service. A distributed database is one that is stored in multiple physical locations. Parts or copies of the database are physically stored in one location and other parts or copies are maintained in other locations. Spanner makes it possible to store information across millions of machines in hundreds of data centers around the globe, with special time-keeping tools to synchronize the data precisely in all of its locations and ensure the data are always consistent. Google uses Spanner to support its various cloud services, including Google Photos, AdWords (Google’s online ad system), and Gmail, and is now making the technology available to other companies that might need such capabilities to run a global business.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed database technology that enables firms and organizations to create and verify transactions on a network nearly instantaneously without a central authority. The system stores transactions as a distributed ledger among a network of computers The information held in the database is continually reconciled by the computers in the network.
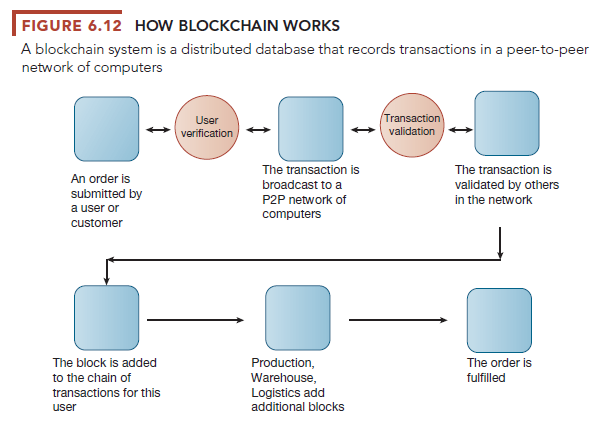
The blockchain maintains a continuously growing list of records called blocks. Each block contains a timestamp and link to a previous block. Once a block of data is recorded on the blockchain ledger, it cannot be altered retroactively. When someone wants to add a transaction, participants in the network (all of whom have copies of the existing blockchain) run algorithms to evaluate and verify the proposed transaction. Legitimate changes to the ledger are recorded across the blockchain in a matter of seconds or minutes and records are protected through cryptography. What makes a blockchain system possible and attractive to business firms is encryption and authentication of the actors and participating firms, which ensures that only legitimate actors can enter information, and only validated transactions are accepted. Once recorded, the transaction cannot be changed. Figure 6.12 illustrates how blockchain works for fulfilling an order.
There are many large benefits to firms using blockchain databases. Blockchain networks radically reduce the cost of verifying users, validating transactions, and the risks of storing and processing transaction information across thousands of firms. Instead of thousands of firms building their own private transaction systems, then integrating them with suppliers, shippers, and financial institution systems, blockchain can provide a single, simple, low-cost transaction system for participating firms. Standardization of recording transactions is aided through the use of smart contracts. Smart contracts are computer programs that implement the rules governing transactions between firms, e.g., what is the price of products, how will they be shipped, when will the transaction be completed, who will finance the transaction, what are financing terms, and the like.
The simplicity and security that blockchain offers has made it attractive for storing and securing financial transactions, supply chain transactions, medical records, and other types of data. Blockchain is a foundation technology for Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies.
Source: Laudon Kenneth C., Laudon Jane Price (2020), Management Information Systems: Managing the Digital Firm, Pearson; 16th edition.

I am not sure the place you’re getting your info, however great topic. I needs to spend some time studying more or figuring out more. Thank you for magnificent info I was on the lookout for this information for my mission.