In addition to the price indexes described in the preceding sections, other types of indexes are useful. In particular, one other application of index numbers is to measure changes in quantity levels over time. This type of index is called a quantity index.
Recall that in the development of the weighted aggregate price index in Section 20.2, to compute an index number for period t we needed data on unit prices at a base period (P0) and period t (Pt). Equation (20.3) provided the weighted aggregate price index as
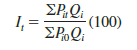
The numerator, OPitQ, represents the total value of fixed quantities of the index items in period t. The denominator, OPi0Qi, represents the total value of the same fixed quantities of the index items in a base period.
Computation of a weighted aggregate quantity index is similar to that of a weighted aggregate price index. Quantities for each item are measured in the base period and period t, with Qi0 and Qit, respectively, representing those quantities for item i. The quantities are then weighted by a fixed price, the value added, or some other factor. The “value added” to a product is the sales value minus the cost of purchased inputs. The formula for computing a weighted aggregate quantity index for period t is

In some quantity indexes the weight for item i is taken to be the base-period price (Pi0), in which case the weighted aggregate quantity index is

Quantity indexes can also be computed on the basis of weighted quantity relatives. One formula for this version of a quantity index follows.
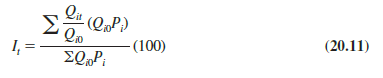
This formula is the quantity version of the weighted price relatives formula developed in Section 20.3 as in equation (20.8).
The Industrial Production Index, developed by the Federal Reserve Board, is probably the best-known quantity index. It is reported monthly and the base period is 2012. The index is designed to measure changes in volume of production levels for a variety of manufacturing classifications in addition to mining and utilities. In May 2018 the index was 107.3.
Source: Anderson David R., Sweeney Dennis J., Williams Thomas A. (2019), Statistics for Business & Economics, Cengage Learning; 14th edition.

28 Aug 2021
30 Aug 2021
28 Aug 2021
31 Aug 2021
30 Aug 2021
30 Aug 2021