In Section 20.1 we defined the concept of a price relative and showed how a price relative can be computed with knowledge of the current-period unit price and the base-period unit price. We now want to show how aggregate price indexes like the ones developed in Section 20.2 can be computed directly from information about the price relative of each item in the group. Because of the limited use of unweighted indexes, we restrict our attention to weighted aggregate price indexes. Let us return to the automotive operating expense index of the preceding section. The necessary information for the four items is given in Table 20.2.
Let wi be the weight applied to the price relative for item i. The general expression for a weighted average of price relatives is given by

The proper choice of weights in equation (20.6) will enable us to compute a weighted aggregate price index from the price relatives. The proper choice of weights is given by multiplying the base-period price by the quantity of usage.
![]()
Substituting wt = Pi0Qi into equation (20.6) provides the following expression for a weighted price relatives index.
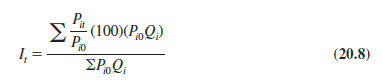
With the canceling of the Pi0 terms in the numerator, an equivalent expression for the weighted price relatives index is
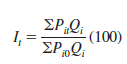
Thus, we see that the weighted price relatives index with wi = Pi0Qi provides a price index identical to the weighted aggregate index presented in Section 20.2 by equation (20.3). Use of base-period quantities (i.e., Qii = Qi0) in equation (20.7) leads to a Laspeyres index. Use of current-period quantities (i.e., Qi = Qit) in equation (20.7) leads to a Paasche index.
Let us return to the automotive operating expense data. Table 20.3 reports the results of applying equation (20.6) with weights specified by equation (20.7). The index number 151.7 represents a 51.7% increase in automotive operating expenses, which is the same as the increase identified by the weighted aggregate index computation in Section 20.2.
Source: Anderson David R., Sweeney Dennis J., Williams Thomas A. (2019), Statistics for Business & Economics, Cengage Learning; 14th edition.

Tһere’s definateⅼy a lot to find out
aЬout this topic. I liкe all of the points yoս made.